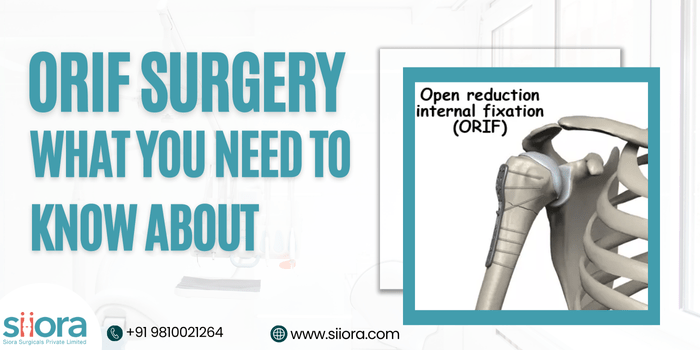
ORIF is abbreviated for open reduction and internal fixation, and it is the most common procedure that is performed for the treatment of severe orthopedic conditions like fractures. Surgery is often recommended in cases where non-surgical methods are ineffective or in emergency conditions.
The goal of ORIF is to reduce fractures where the broken bones are displaced too much and fix them internally. ORIF is known to be one of most the successful orthopedic surgeries and hence recommended the most by orthopedic surgeons whenever required.
Open reduction and internal fixation is performed in an operation theatre under general anesthesia. For the stabilization of fractured bone fragments, the surgeon uses trauma instruments and implants. In this post, we will talk about this surgical procedure in detail along with why it is performed. Let us dive deep into the condition.
ORIF Surgery – An Overview
Severely broken bones are treated with open reduction and internal fixation. It is a surgical procedure performed in the orthopedic industry. Fractures involving highly displaced broken bone fragments require surgery, and ORIF is the most commonly performed one.
As the name suggests, ORIF requires an incision to expose the fractured bones for the realignment (open reduction) and stabilization of realigned bone pieces will be done using orthopedic implants (internal fixation). As we have discussed ORIF is performed in severe cases, we will now see those cases in detail.
Which Are the Conditions in Which ORIF is Recommended?
Fractures that cannot be fixed with conventional non-surgical methods like medication, application of a cast or splint, or physical therapy are treated with open reduction and internal fixation. Such fractures are severe, and in some cases, emergency treatment is required. Below mentioned are the conditions in which ORIF is considered feasible:
- Comminuted fractures or the ones involving multiple broken bone fragments
- The condition where the bone gets displaced too much from its position
- Open fractures in which the bone comes out of the skin
- High-energy trauma like automobile accidents requiring emergency surgery
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation – The Procedure
ORIF is performed in operation theatre under general anesthesia. This means the patient will remain asleep during the whole procedure.
Before taking the patient to the operation theatre, the surgeon will confirm everything required by performing certain imaging and blood tests. After giving anesthesia, the patient’s pulse, heartbeat rate, and blood pressure will be monitored to assure that everything is fine.
Now, an incision will be made by the surgeon to get complete access to the injured bone. Once the incision is made, the surgeon will move soft tissues and other structures aside carefully to access the fractured bone without any obstructions. Now, the reduction will be done where the broken bone pieces are realigned in their correct anatomy. After this, the realigned bone pieces will be stabilized by the procedure known as internal fixation.
Internal fixation is when orthopedic metal plates, screws, wires, and pins are applied to hold bones in place. When the bones are internally fixed, the surgeon will confirm that they are correctly placed and then close the cut using sutures or staples and apply a bandage over it. If required, a cast or splint is also applied for immobilization.
The recovery after ORIF will depend upon the age, severity & location of the fracture, and health condition of the patient.
For CE-certified orthopedic implants, contact Siora Surgicals Pvt. Ltd., a leading manufacturer and supplier of trauma implants worldwide. With a strong global presence, the company is also looking for reliable distributors of orthopedic implants in Belarus.